Fibroid
- Home
- / Fibroid
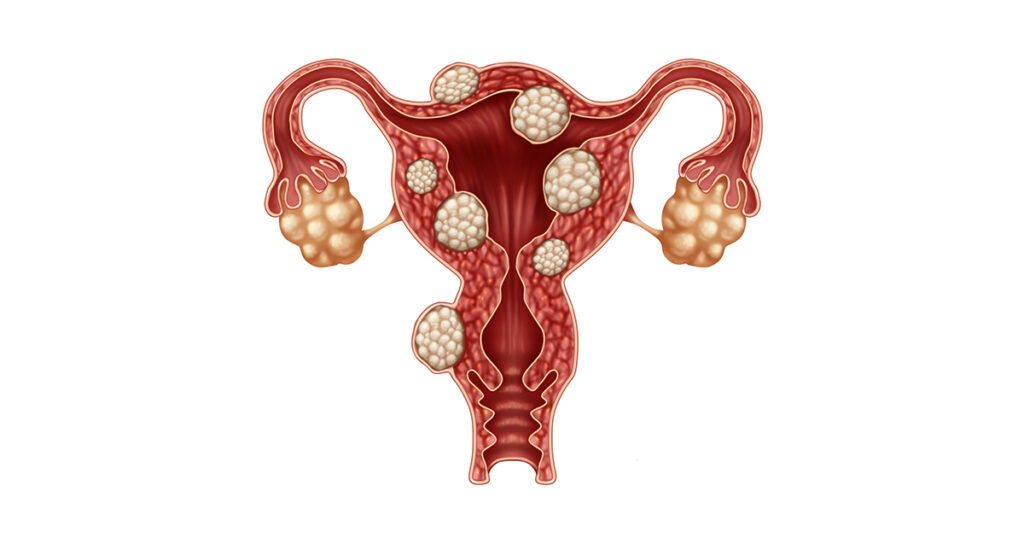
Fibroid
Symptoms
Heavy Menstrual Bleeding: Often leading to anemia.
Prolonged Menstrual Periods: Lasting more than a week.
Pelvic Pain or Pressure: A feeling of fullness in the lower abdomen.
Frequent Urination: Due to pressure on the bladder.
Difficulty Emptying the Bladder.
Constipation.
Backache or Leg Pains: If fibroids press on nerves.
Pain During Intercourse.
Reproductive Issues: Infertility, multiple miscarriages, or complications during pregnancy.
Treatment
Observation
Many women with fibroids experience no symptoms or only mild symptoms and may not need treatment. Fibroids often shrink after menopause.
Medications
Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone (GnRH) Agonists: Reduce fibroid size by lowering estrogen and progesterone levels.
Progestin-Releasing Intrauterine Device (IUD): Helps relieve heavy bleeding.
Other Medications: NSAIDs, oral contraceptives, or progestins to control symptoms.
Non-Invasive Procedures
MRI-Guided Focused Ultrasound Surgery (FUS): Uses high-frequency sound waves to destroy fibroid tissue.
Minimally Invasive Procedures
Uterine Artery Embolization: Blocks the blood supply to fibroids to shrink them.
Myolysis: Uses electric current or laser to destroy fibroids.
Laparoscopic or Robotic Myomectomy: Removes fibroids while preserving the uterus.
Hysteroscopic Myomectomy: Removes fibroids through the vagina and cervix using a hysteroscope.
